| WAS Version | SOAP PORT |
| Version 8 Deployment Manager | 8879 |
| Version 8 AppServer | 8880 |
| Version 8 Node agent | 8878 |
| Version 7 Deployment Manager | 8879 |
| Version 7 AppServer | 8880 |
| Version 7 Node agent | 8878 |
| Version 6.1 Deployment Manager | 8879 |
| Version 6.1 AppServer | 8880 |
| Version 6.1 Node agent | 8879 |
| Version 6.0 Deployment Manager | 8879 |
| Version 6.0 AppServer | 8880 |
| Version 6.0 Node Agent | 8878 |
| Version 5.0 Deployment Manager | 8879 |
| Version 5.0 Node Agent | 8880 |
| Version 5.0 AppServer | 8878 |
SOAP PORT Details of WebSphere Application Server
Baisc construct for MQ messaging - A Practical Approach.
This example is a simple demonstration for understanding how MQ transfer messages between two queue managers and the minimum required MQ components for the same.
Kindly Share/Like/Follow the page if you like this article.
Below are the steps involved in this example.Source queue manager
------------------------------
1.) Create source queue manager.
2.) Start source queue manager.
3.) Connect to source queue manager using runmqsc command.
4.) Create a listener in source queue manager.
5.) Create transmission queue in source queue manager.
6.) Create a remote queue in source queue manager.
7.) Create a sender channel in source queue manager.
8.) Quit MQSC
Destination queue manager
-------------------------------------
1.) Create destination queue manager.
2.) Start destination queue manager.
3.) Connect to destination queue manager using runmqsc command.
4.) Create a listener in destination queue manager.
5.) Create a receiver channel in destination queue manager.
6.) Create a local queue in destination queue manager.
7.) Quit MQSC.
Restart Source & Destination Queue Managers.
-------------------------------------------------------------
1.) Stop source queue manager.
2.) Stop destination queue manager.
3.) Start source queue manager.
3.a.) Make sure that the listener started for source queue manager , if not start the listener.
4.) start destination queue manager.
4.a.) Make sure that the listener started for destination queue manager, if not start the listener.
5.) Connect to source queue manager using runmqsc command.
6.) Start sender channel on source queue manager.
7.) Check the channel status of both queue managers and make sure that both channels are running..
8.) Quit MQSC.
Testing
----------
1.) Put a message in remote queue of source queue manager.
2.) browse/get messages from local queue of destination queue manager.
Now let us implement above steps in a test server.
A.) Source queue manager (MqM1)
---------------------------------------------
1.) Create source queue manager MqM1
[root@myhost mqm]# crtmqm MqM1
WebSphere MQ queue manager created.
Directory '/var/mqm/qmgrs/MqM1' created.
Creating or replacing default objects for MqM1.
Default objects statistics : 65 created. 0 replaced. 0 failed.
Completing setup.
Setup completed.
2.) Start source queue manager MqM1
[root@myhost mqm]# strmqm MqM1
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM1' starting.
5 log records accessed on queue manager 'MqM1' during the log replay phase.
Log replay for queue manager 'MqM1' complete.
Transaction manager state recovered for queue manager 'MqM1'.
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM1' started.
3.) Connect to source queue manager MqM1 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM1
5724-H72 (C) Copyright IBM Corp. 1994, 2009. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Starting MQSC for queue manager MqM1.
4.) Create a listener in source queue manager MqM1.
define listener ('MqM1.LSNR') TRPTYPE( TCP ) PORT (1486)
1 : define listener ('MqM1.LSNR') TRPTYPE( TCP ) PORT (1486)
AMQ8626: WebSphere MQ listener created.
5.) Create transmition queue in source queue manager.
define qlocal ('TR1.MqM1.Q1') USAGE (XMITQ)
2 : define qlocal ('TR1.MqM1.Q1') USAGE (XMITQ)
AMQ8006: WebSphere MQ queue created.
6.) Create a remote queue in source queue manager.
define qremote ('RMT.MqM1.Q1') XMITQ ('TR1.MqM1.Q1') RQMNAME('MqM2') RNAME('LOC.MqM2.Q1')
3 : define qremote ('RMT.MqM1.Q1') XMITQ ('TR1.MqM1.Q1') RQMNAME(MqM2) RNAME('LOC.MqM2.Q1')
AMQ8006: WebSphere MQ queue created.
Points to be noted:-
XMITQ :- Should be the same name mentioned while creating transmission queue in step A.5
RQMNAME :- Specify the same name mentioned while creating destination queue manager B.1
7.) Create a sender channel in source queue manager.
define channel ('MqM1.SNDR') CHLTYPE(SDR) CONNAME('localhost(1487)') XMITQ('TR1.MqM1.Q1')
4 : define channel ('MqM1.SNDR') CHLTYPE(SDR) CONNAME('localhost(1487)') XMITQ('TR1.MqM1.Q1')
AMQ8014: WebSphere MQ channel created.
Points to be noted:-
XMITQ :- Should be the same name mentioned while creating transmission queue in step A.5
CONNAME:- Specify the hostname/ipaddress and port number of the remote queue manager
8.) Quit MQSC
end
B.) Destination queue manager (MqM2)
----------------------------------------------------
1.) Create destination queue manager MqM2
[root@myhost mqm]# crtmqm MqM2
WebSphere MQ queue manager created.
Directory '/var/mqm/qmgrs/MqM2' created.
Creating or replacing default objects for MqM2.
Default objects statistics : 65 created. 0 replaced. 0 failed.
Completing setup.
Setup completed.
2.) Start destination queue manager MqM2
[root@myhost mqm]# strmqm MqM2
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM2' starting.
5 log records accessed on queue manager 'MqM2' during the log replay phase.
Log replay for queue manager 'MqM2' complete.
Transaction manager state recovered for queue manager 'MqM2'.
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM2' started.
3.) Connect to destination queue manager MqM2 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM2
5724-H72 (C) Copyright IBM Corp. 1994, 2009. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Starting MQSC for queue manager MqM2.
4.) Create a listener in destination queue manager.
define listener ('MqM2.LSNR') TRPTYPE( TCP ) PORT (1487)
1 : define listener ('MqM2.LSNR') TRPTYPE( TCP ) PORT (1487)
AMQ8626: WebSphere MQ listener created.
5.) Create a receiver channel in destination queue manager.
define channel ('MqM1.SNDR') CHLTYPE(RCVR)
2 : define channel ('MqM1.SNDR') CHLTYPE(RCVR)
AMQ8014: WebSphere MQ channel created.
Points to be noted:-
Channel name should be the same name mentioned while creating channel in step A.7
6.) Create a local queue in destination queue manager.
define qlocal ('LOC.MqM2.Q1')
3 : define qlocal ('LOC.MqM2.Q1')
AMQ8006: WebSphere MQ queue created.
7.) Quit MQSC
end
C.) Restart Source and Destination Queue Managers
--------------------------------------------------------------------
1.) Stop source queue manager MqM1.
[root@myhost mqm]# endmqm MqM1
Quiesce request accepted. The queue manager will stop when all outstanding work is complete.
2.) Stop destination queue manager MqM2.
[root@myhost mqm]# endmqm MqM2
Quiesce request accepted. The queue manager will stop when all outstanding work is complete.
3.) Start source queue manager MqM1.
[root@myhost mqm]# strmqm MqM1
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM1' starting.
5 log records accessed on queue manager 'MqM1' during the log replay phase.
Log replay for queue manager 'MqM1' complete.
Transaction manager state recovered for queue manager 'MqM1'.
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM1' started.
4.) Start destination queue manager MqM2
[root@myhost mqm]# strmqm MqM2
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM2' starting.
5 log records accessed on queue manager 'MqM2' during the log replay phase.
Log replay for queue manager 'MqM2' complete.
Transaction manager state recovered for queue manager 'MqM2'.
WebSphere MQ queue manager 'MqM2' started.
5.) Connect to source queue manager MqM1 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM1
5724-H72 (C) Copyright IBM Corp. 1994, 2009. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Starting MQSC for queue manager MqM1.
6.) Start sender channel on source queue manager.
start channel ('MqM1.SNDR')
1 : start channel ('MqM1.SNDR')
AMQ8018: Start WebSphere MQ channel accepted.
Points to be noted:- Starting sender channel will start the receiver channel automatically.
Step D contains the steps to check channel status.
NOTE:-
Make sure that listeners are started, if not started use below steps to start listeners
1.) Connect to source queue manager MqM1 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM1
2.) Verify Listener 'MqM1.LSNR' is running in source queue manager MqM1
display lsstatus ('MqM1.LSNR')
2.a.) If the listener 'MqM1.LSNR' is not running start it by using below mqsc command
start listener ('MqM1.LSNR')
1 : start listener ('MqM1.LSNR')
AMQ8021: Request to start WebSphere MQ Listener accepted.
3.) Quit MQSC
end
4.) Connect to destination queue manager MqM2 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM2
5.) Verify listener 'MqM2.LSNR' is running in destination queue manager MqM2

5.a.) If the listener 'MqM2.LSNR' is not running start it by using below mqsc command
1 : start listener ('MqM1.LSNR')
AMQ8021: Request to start WebSphere MQ Listener accepted.
3.) Quit MQSC
end
4.) Connect to destination queue manager MqM2 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM2
5.) Verify listener 'MqM2.LSNR' is running in destination queue manager MqM2

5.a.) If the listener 'MqM2.LSNR' is not running start it by using below mqsc command
start listener ('MqM2.LSNR')
1 : start listener ('MqM2.LSNR')
AMQ8021: Request to start WebSphere MQ Listener accepted.
D.) Checking channel status of both Qmgr
------------------------------------------------------
1.)Connect to source queue manager MqM1 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM1
2.) Verify the channel 'MqM1.SNDR' status
display chstatus ('MqM1.SNDR')
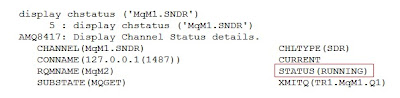
1 : start listener ('MqM2.LSNR')
AMQ8021: Request to start WebSphere MQ Listener accepted.
D.) Checking channel status of both Qmgr
------------------------------------------------------
1.)Connect to source queue manager MqM1 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM1
2.) Verify the channel 'MqM1.SNDR' status
display chstatus ('MqM1.SNDR')

3.) Quit MQSC
4.) Connect to destination queue manager MqM2 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM2
5.) Verify the channel 'MqM1.SNDR' status
display chstatus ('MqM1.SNDR')
4.) Connect to destination queue manager MqM2 using runmqsc command.
[root@myhost mqm]# runmqsc MqM2
5.) Verify the channel 'MqM1.SNDR' status
display chstatus ('MqM1.SNDR')
E.) Testing the setup
---------------------------
Note:- If not already installed, Install the samples before proceeding with below test.
1.) Put a message in remote Queue of MqM1
/opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsput RMT.MqM1.Q1 MqM1
Type below text
This is a test message from RMT.MqM1.Q1 (remote Queue) of MqM1 to LOC.MqM2.Q1 (Local Queue) of MqM2
Press ctrl+z
Eg:-
[root@myhost bin]# /opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsput RMT.MqM1.Q1 MqM1
Sample AMQSPUT0 start
target queue is RMT.MqM1.Q1
This is a test message from RMT.MqM1.Q1 (remote Queue) of MqM1 to LOC.MqM2.Q1 (Local Queue) of MqM2
[2]+ Stopped /opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsput RMT.MqM1.Q1 MqM1
[root@myhost bin]#
2.) Browse/get the message from Local Queue of MqM2.
Note:- If not already installed, Install the samples before proceeding with below test.
1.) Put a message in remote Queue of MqM1
/opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsput RMT.MqM1.Q1 MqM1
Type below text
This is a test message from RMT.MqM1.Q1 (remote Queue) of MqM1 to LOC.MqM2.Q1 (Local Queue) of MqM2
Press ctrl+z
Eg:-
[root@myhost bin]# /opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsput RMT.MqM1.Q1 MqM1
Sample AMQSPUT0 start
target queue is RMT.MqM1.Q1
This is a test message from RMT.MqM1.Q1 (remote Queue) of MqM1 to LOC.MqM2.Q1 (Local Queue) of MqM2
[2]+ Stopped /opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsput RMT.MqM1.Q1 MqM1
[root@myhost bin]#
2.) Browse/get the message from Local Queue of MqM2.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
/opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsget LOC.MqM2.Q1 MqM2
[root@myhost bin]# /opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsget LOC.MqM2.Q1 MqM2
Sample AMQSGET0 start
message <This is a test message from RMT.MqM1.Q1 (remote Queue) of MqM1 to LOC.MqM2.Q1 (Local Queue) of MqM2>
/opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsget LOC.MqM2.Q1 MqM2
[root@myhost bin]# /opt/mqm/samp/bin/amqsget LOC.MqM2.Q1 MqM2
Sample AMQSGET0 start
message <This is a test message from RMT.MqM1.Q1 (remote Queue) of MqM1 to LOC.MqM2.Q1 (Local Queue) of MqM2>
no more messages
Sample AMQSGET0 end
[root@myhost bin]#
Sample AMQSGET0 end
[root@myhost bin]#
Kindly Like/Follow the page if you like this article.
Request you to post your comments so that I can improve the content.
JVM heap size/properties by using wsadmin utillity
How to get JVM heap size/properties by using wsadmin utillity
------------------------------
1.)Type below command from wsadmin prompt
------------------------------
wsadmin>$AdminTask showJVMProperties {-serverName server1 -nodeName myhostNode01}
Output
--------
{classpath {}} {bootClasspath {}} {verboseModeClass false} {verboseModeGarbageCollection false} {verboseModeJNI false} {initialHeapSize 258} {maximumHeapSize 512} {runHProf false} {hprofArguments {}} {debugMode false} {debugArgs -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_so
OR
2.)Type below command from the OS prompt
------------------------------
[root@myhost bin]# ./wsadmin.sh -c '$AdminTask showJVMProperties {-serverName server1 -nodeName
myhostNode01}'
Output
--------
Realm/Cell Name: <default>
Username: root
Password:
WASX7209I: Connected to process "dmgr" on node myhostCellManager01 using SOAP connector; The type of process is: DeploymentManager
{classpath {}} {bootClasspath {}} {verboseModeClass false} {verboseModeGarbageCollection false} {verboseModeJNI false} {initialHeapSize 258} {maximumHeapSize 512} {runHProf false} {hprofArguments {}} {debugMode false} {debugArgs -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_so
OR
3.)Type below command from the OS prompt
------------------------------
[root@myhost bin]# ./wsadmin.sh -c "\$AdminTask showJVMProperties {-serverName server1 -nodeName
myhostNode01}"
Output
---------
Realm/Cell Name: <default>
Username: root
Password:
WASX7209I: Connected to process "dmgr" on node
myhostCellManager01 using SOAP connector; The type of process is: DeploymentManager
{classpath {}} {bootClasspath {}} {verboseModeClass false} {verboseModeGarbageCollection false} {verboseModeJNI false} {initialHeapSize 258} {maximumHeapSize 512} {runHProf false} {hprofArguments {}} {debugMode false} {debugArgs -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_so
Note:- Kindly note that the difference between second and third command is only the quotes,Commands
inside a double quotes require \ prefix for $ symbol.
------------------------------
1.)Type below command from wsadmin prompt
------------------------------
wsadmin>$AdminTask showJVMProperties {-serverName server1 -nodeName myhostNode01}
Output
--------
{classpath {}} {bootClasspath {}} {verboseModeClass false} {verboseModeGarbageCollection false} {verboseModeJNI false} {initialHeapSize 258} {maximumHeapSize 512} {runHProf false} {hprofArguments {}} {debugMode false} {debugArgs -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_so
OR
2.)Type below command from the OS prompt
------------------------------
[root@myhost bin]# ./wsadmin.sh -c '$AdminTask showJVMProperties {-serverName server1 -nodeName
myhostNode01}'
Output
--------
Realm/Cell Name: <default>
Username: root
Password:
WASX7209I: Connected to process "dmgr" on node myhostCellManager01 using SOAP connector; The type of process is: DeploymentManager
{classpath {}} {bootClasspath {}} {verboseModeClass false} {verboseModeGarbageCollection false} {verboseModeJNI false} {initialHeapSize 258} {maximumHeapSize 512} {runHProf false} {hprofArguments {}} {debugMode false} {debugArgs -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_so
OR
3.)Type below command from the OS prompt
------------------------------
[root@myhost bin]# ./wsadmin.sh -c "\$AdminTask showJVMProperties {-serverName server1 -nodeName
myhostNode01}"
Output
---------
Realm/Cell Name: <default>
Username: root
Password:
WASX7209I: Connected to process "dmgr" on node
myhostCellManager01 using SOAP connector; The type of process is: DeploymentManager
{classpath {}} {bootClasspath {}} {verboseModeClass false} {verboseModeGarbageCollection false} {verboseModeJNI false} {initialHeapSize 258} {maximumHeapSize 512} {runHProf false} {hprofArguments {}} {debugMode false} {debugArgs -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_so
Note:- Kindly note that the difference between second and third command is only the quotes,Commands
inside a double quotes require \ prefix for $ symbol.
Schedule your job using crontab
CRONTAB ---> Kindly post your commends/Likes.
crontab command options
------------------------------
... crontab -e Edit/Create crontab file
crontab -l Display crontab file.
crontab -r Remove crontab file.
crintab file syntax
-------------------
* * * * * <command>
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | Day of the week Range--->(0-6) [Sunday=0]
| | | Month Range---> (1-12)
| | Day of month Range---> (1-31)
| Hour Range ---> (0-23)
Min Range---> (0-59)
* implies all legal values corresponding to that field.
Eg:
30 11 1 * * /home/prasanth/logBackup.sh
As per the above schedule logBackup.sh will run at every month (* in month field) Day 1 (1 in Day of the month) 11 Hours (11 in hour field) 30 mins (30 in min field)
Note: If an users name appears in the cron.deny file that user will not be able to run any crons, If an user exists in th ecron.allow file that user is allowed to run the cron
crontab command options
------------------------------
... crontab -e Edit/Create crontab file
crontab -l Display crontab file.
crontab -r Remove crontab file.
crintab file syntax
-------------------
* * * * * <command>
- - - - -
| | | | |
| | | | Day of the week Range--->(0-6) [Sunday=0]
| | | Month Range---> (1-12)
| | Day of month Range---> (1-31)
| Hour Range ---> (0-23)
Min Range---> (0-59)
* implies all legal values corresponding to that field.
Eg:
30 11 1 * * /home/prasanth/logBackup.sh
As per the above schedule logBackup.sh will run at every month (* in month field) Day 1 (1 in Day of the month) 11 Hours (11 in hour field) 30 mins (30 in min field)
Note: If an users name appears in the cron.deny file that user will not be able to run any crons, If an user exists in th ecron.allow file that user is allowed to run the cron
WAS,IHS and Plugin log Details
Kindly post your comments and likes.
IBM Http Server Logs.
=================
Default log Directory
--------------------------
<IHS_Install_Root>/logs
access.log --> Contains the logs of all requests process by IBM Http Server.
error.log ----> Contains the errors and diagnostics information while processing the requests.
Plugin Logs.
========
Default Log Directory.
---------------------------
<Plugin_Install_Root>/logs
http_plugin.log ---> Contains the logs of plugin errors.
WebSphere Application Server Logs.
===========================
Default log Location.
--------------------------
<LOG_ROOT> = <WAS_Profile_Root>/logs/
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT> = <WAS_Profile_Root>/logs/
for Eg: If the WAS profile location is "/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppSever/
<LOG_ROOT> = "/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppSever/
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT> = "/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppSever/
Trace Logs.
-------------
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/trace.log ---> Contains the trace information if the trace is enabled.
JVM Logs.
-----------
These logs are created by redirecting output and error streams of JVM into independent log files. The SystemOut.log file contains the logs used to monitor the health of running application server. SystemErr.log contains the exceptions. Every application servers and all of its application will have these two sets of files.
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>\SystemOut.lo
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/
Process Logs.
----------------
The application server writes output and error streams of native processes into these logs.This may also contain the information related to problemes in native codes.
If the Verbose GC is enabled, GC informations are written into these logs.
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/
IBM Service Logs.
--------------------
This is a binary log and it need Log Analyzer tool to analyze. There will be only one activity log for a single node ( for all JVMs and nodeagents).
IBM Service Log contains the information written to System.out by the Application Server run time as well as special messages that contain extended service information. These logs are mainly used by IBM service team for solving complex issues.
<LOG_ROOT>/activity.log
IBM Http Server Logs.
=================
Default log Directory
--------------------------
<IHS_Install_Root>/logs
access.log --> Contains the logs of all requests process by IBM Http Server.
error.log ----> Contains the errors and diagnostics information while processing the requests.
Plugin Logs.
========
Default Log Directory.
---------------------------
<Plugin_Install_Root>/logs
http_plugin.log ---> Contains the logs of plugin errors.
WebSphere Application Server Logs.
===========================
Default log Location.
--------------------------
<LOG_ROOT> = <WAS_Profile_Root>/logs/
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT> = <WAS_Profile_Root>/logs/
for Eg: If the WAS profile location is "/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppSever/
<LOG_ROOT> = "/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppSever/
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT> = "/usr/IBM/WebSphere/AppSever/
Trace Logs.
-------------
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/trace.log ---> Contains the trace information if the trace is enabled.
JVM Logs.
-----------
These logs are created by redirecting output and error streams of JVM into independent log files. The SystemOut.log file contains the logs used to monitor the health of running application server. SystemErr.log contains the exceptions. Every application servers and all of its application will have these two sets of files.
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>\SystemOut.lo
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/
Process Logs.
----------------
The application server writes output and error streams of native processes into these logs.This may also contain the information related to problemes in native codes.
If the Verbose GC is enabled, GC informations are written into these logs.
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/
<SERVER_LOG_ROOT>/
IBM Service Logs.
--------------------
This is a binary log and it need Log Analyzer tool to analyze. There will be only one activity log for a single node ( for all JVMs and nodeagents).
IBM Service Log contains the information written to System.out by the Application Server run time as well as special messages that contain extended service information. These logs are mainly used by IBM service team for solving complex issues.
<LOG_ROOT>/activity.log
WAS Version Details
WAS Version Details
--------------------------
Let us check how a version number is formed..
For example: Let us take version 6.0.2.13
----6--------- 0 ------------2 -----------13---
version | release | refresh pack | fixpack
--------------------------
Let us check how a version number is formed..
For example: Let us take version 6.0.2.13
----6--------- 0 ------------2 -----------13---
version | release | refresh pack | fixpack
Encoding password value in soap.client.props file
Encoding password value in soap.client.props file
------------------------------
Change directory to 'properties' and then issue below command
../bin/
------------------------------
Change directory to 'properties' and then issue below command
../bin/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

